What is the difference between FPV and drone?
2024-07-29 18:07:38
Some friends may think that FPVdrone and drones are the same thing, which is really wrong! Let me give you a science popularization, in fact, the two of them are very different.
What is a FPVdrone?

The history and development of the drone can be traced back to the end of the 20th century, when drone technology began to gradually mature, laying the foundation for the birth of the machine. With the rapid development of microelectronics and wireless communication technology, the design and manufacture of drones have become more sophisticated and efficient.
At the beginning of the 21st century, with the introduction of FPV (First Person View) technology, the FPV began to become popular among enthusiasts and became an emerging form of entertainment. With the continuous advancement of technology, such as lighter and stronger materials, more efficient batteries and more advanced flight control systems, the performance of the drone has been greatly improved, and its application in the field of scientific research and exploration has also been promoted. For example, PFV machines are becoming more and more widely used in environmental monitoring, disaster assessment, and archaeological exploration, showing great potential in a number of fields.
What is the difference between FPV and drone?
01Different uses and performance:
FPV: This type of aircraft is mainly designed for competition, entertainment, and extreme flying, and is characterized by high speed, strong maneuverability, and responsiveness. The drone is capable of high-speed acceleration, precise steering, and complex tumbling in a fraction of the time, providing extreme flight flexibility and an immersive first-person view (FPV) flight experience. Usually, the drone is small in size, has a limited battery life, and mostly adopts DIY assembly to meet the needs of personalized customization and performance optimization.
Unmanned aerial vehicles: covering a wider range, from consumer to industrial level, application fields include aerial photography, remote sensing mapping, agricultural plant protection, logistics and distribution, security patrol, scientific research experiments, etc. Drones usually focus on stability, endurance and payload, and in many cases need to carry cameras, sensors and other equipment for data collection, so they are designed to focus more on reliability and practicality.
02 Different Structural Complexity:

FPV: Compact design with a focus on weight reduction and improved dynamics, typically made of lightweight materials, high-speed brushless motors, high-performance ESCs, and a streamlined flight control system.
Drones: In addition to the basic flight system, it may also integrate advanced navigation systems, obstacle avoidance systems, visual positioning systems, etc., as well as larger capacity batteries and more stable structures to adapt to various harsh environments.
03 Different control methods:
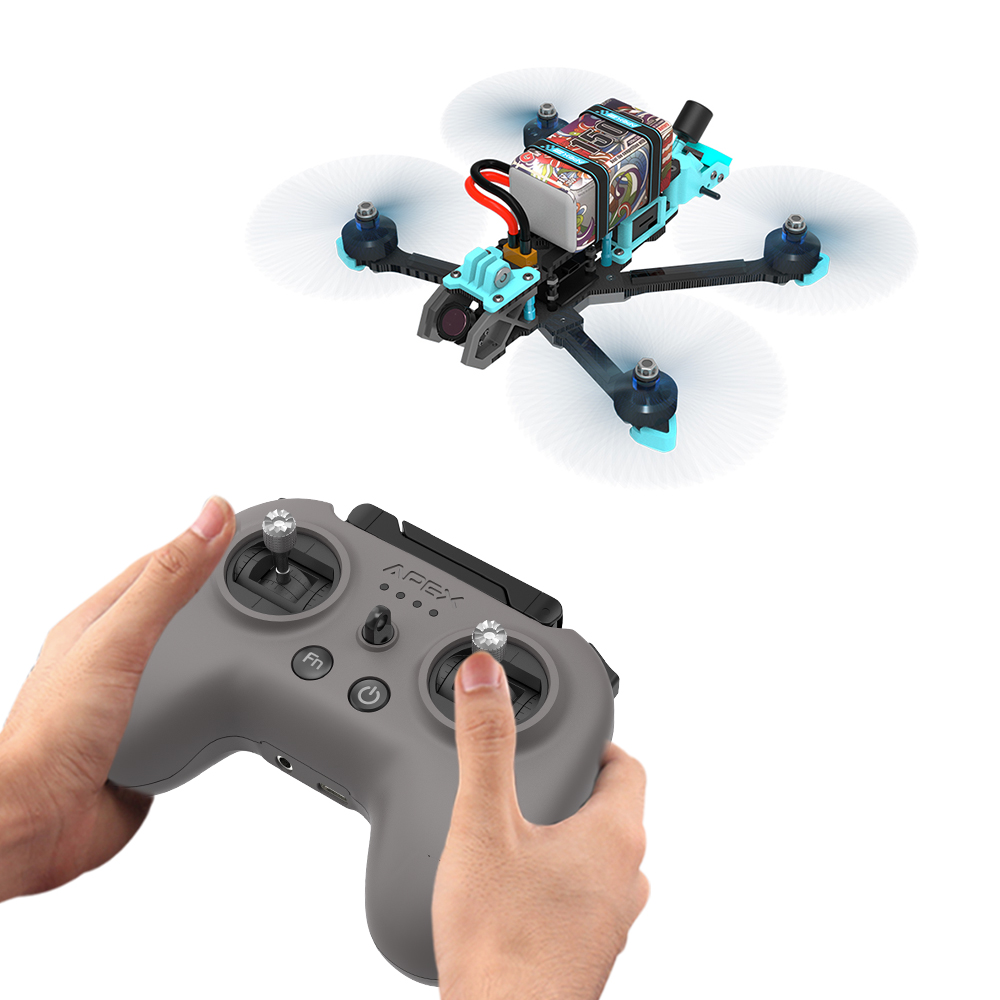

FPV: First-person perspective flight is usually achieved through FPV glasses, and the controller can observe the scene in front of the aircraft in real time, and operate with a high-speed responsive handle or joystick, which requires high control skills.
Drones: They can be remotely controlled via remote control or ground station software, or they can preset flight paths and automate tasks, with varying levels of difficulty depending on the model and functional requirements.
04Different application scenarios:
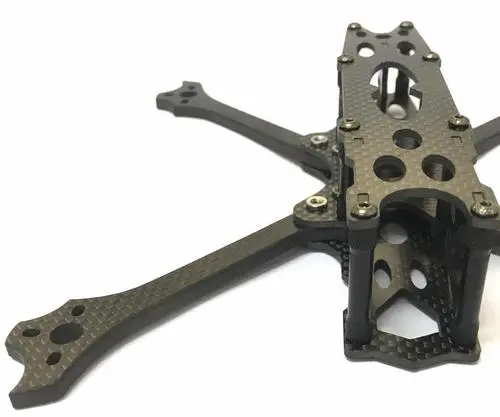

FPV: Mainly used for drone racing, fancy air shows, small item delivery tests, etc., emphasizing speed and agility.
Unmanned aerial vehicles: widely used in commercial, industrial, scientific research, public services and other fields, including aerial photography, geographic mapping, disaster relief, crop monitoring, cargo transportation, etc., focusing on task execution efficiency and data collection quality.
To sum up, FPV mainly focuses on the field of extreme sports and competitive entertainment, and its core feature is the pursuit of the ultimate speed experience and the thrill of control. These aircraft are often designed to meet the needs of pilots who are looking for thrills and challenges. In contrast, drones are designed for a wider range of applications and include not only entertainment, but also into various practical and commercial scenarios. The emphasis on drones is stability and the ability to perform tasks.
So, the next time someone confuses FPV with drones, you can tell them handsomely: "It's not the same thing, FPV is a master of extreme sports in the flying world, and it's all about excitement and skill!" ”